Family membership
Health insurance provides insurance benefits not just to insured persons but also to their dependent family members. These family members are referred to as “dependents”. Family members must meet certain conditions related to “residency in Japan,” “the extent of the family relationship,” and “income” before they are authorized as dependents.
- Tips
-
- Dependents must be certified by the Health Insurance Society.
- If there is any change in your dependents, submit notification of the change within five days.
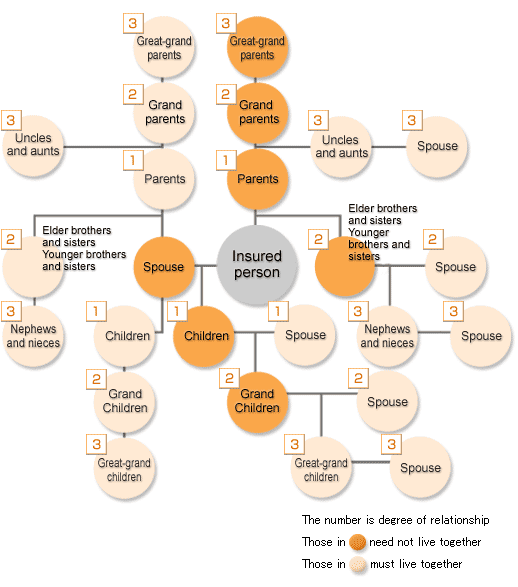
Extent of family relationship
The scope of family members eligible to be certified as dependents is legally defined. Conditions for dependent eligibility also vary depending on whether or not the family member lives with the insured person.
Family members who may live with or apart from the insured person:
- Spouse (including common law spouse)
- Children, grandchildren
- Siblings
- Parents and other lineal ascendants
Family members who must live with the insured person:
- Family members within the third degree of consanguinity other than those above
- Parents and children of the insured person's common law spouse
- Parents and children of deceased common law spouse
Income standards
To be certified as a dependent, the family member must live primarily off the insured person's income, and this is determined based on whether they live together or separately and their annual income.
Regarding the determination of annual income, an age requirement of 19-22 years old has been added, effective October 1, 2025.
| If the family member lives with the insured person | The family member’s annual income must be less than 1.3 million yen (108,334 yen per month), and it must be less than one half the income of the insured person. If the family member is aged 60 or above, or a person with a disability that is eligible for receipt of Disability Employees' Pension benefits, their annual income must be less than 1.8 million yen (150,000 yen per month), and it must be less than one half the income of the insured person. |
|---|---|
| If the family member lives apart from the insured person | The family member’s annual income must be less than 1.3 million yen (108,334 yen per month), and it must be less than the amount of the allowance sent to the family member by the insured person. If the family member is aged 60 or above, or a person with a disability that is eligible for receipt of Disability Employees' Pension benefits, their annual income must be less than 1.8 million yen (150,000 yen per month), and it must be less than the amount of the allowance sent to the family member by the insured person. |
- * In the same way as age is defined under the Income Tax Act, whether a family member is aged 19-22 is determined based on the family member's age as of December 31 of the year. (Note that under the Civil Code, one year is added to your age on the day before your birthday, so for a family member whose birthday is January 1, the family member's age will be increased on December 31.)

Government measures to address annual income barriers (starting in October 2023)
What are annual income barriers?
Annual income barriers refer to threshold income amounts that determine whether or not taxes and social insurance premiums are incurred.
Individuals who have dependent status and work part-time or other non-regular jobs will lose their dependent status if their annual income exceeds a certain figure, and become an insured person under a company health insurance plan, National Health Insurance, or other insurance system. They will then be required to pay social insurance premiums, which may result in lower take-home pay.
One of two different annual income barriers applies for social insurance premiums, depending on company size and other factors: 1.06 million yen or 1.3 million yen.
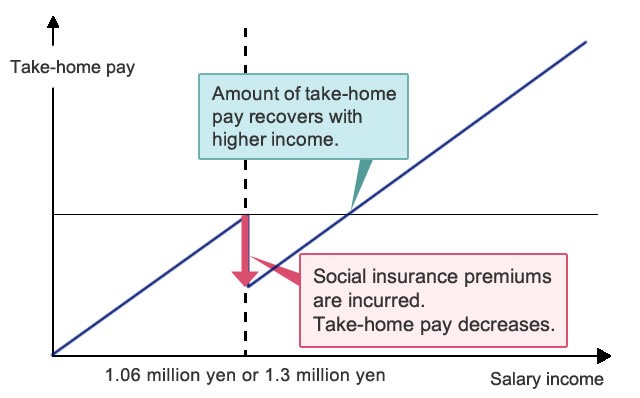
(Source: Provisional measures to address annual income barriers (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare))
| 1.06 million yen annual income barrier | At companies with 51 or more employees, an employee will incur social insurance premiums if certain conditions, such as when monthly wages are 88,000 yen or more (i.e., annual income is approximately 1.06 million yen or more), are satisfied. |
|---|---|
| 1.3 million yen* annual income barrier | Social insurance premiums are incurred automatically without exception, since the worker no longer meets the dependent eligibility criteria. |
- * 1.5 million yen if aged 19-22 [and not the insured person's spouse]; 1.8 million yen if aged 60 or above or with a disability eligible for receipt of Disability Employees' Pension benefits
Handling for the 1.3 million yen annual income barrier
Although dependent certification is based on checking of taxation certificates and other documents from the previous year, if the worker’s annual income is expected to temporarily exceed 1.3 million yen due to longer hours because of labor shortage or other factors, the worker may choose to retain his or her dependent status simply by attaching a certificate from the employer.
(In principle, this handling is available no more than two consecutive times for a single worker.)
Handling for the 1.06 million yen annual income barrier
Companies that help increase worker income through means such as payment of allowances to encourage social insurance coverage* will be provided subsidies for a finite term.
* Allowances to encourage social insurance coverage
These allowances are intended to encourage employee insurance coverage for those working reduced hours and to reduce the burden of insurance premiums when workers who had been ineligible for insurance are newly covered by insurance.
Allowances to encourage social insurance coverage are to be paid apart from salaries and bonuses. They are not considered when calculating the standard monthly remuneration or standard bonuses used to determine insurance premiums.
- * Eligible persons: Those with standard monthly remuneration of 104,000 yen or less
- * Maximum allowance amount excluded from standard remuneration: Amount equivalent to the insurance premiums newly incurred by the employee due to insurance coverage
- * A time-limited measure not to exceed two years
New requirement concerning residency in Japan for dependent certification
From April 2020, a requirement related to residency in Japan is added to the requirements for certification of health insurance dependents. In principle, from April 1, 2020, those who do not have addresses in Japan cannot be certified as dependents (with certain exceptions?for example, students studying abroad).
Rationale underlying the domestic residency requirement
Determinations of residency are based on whether a person is registered to the basic resident register (i.e., whether or not the person has a certificate of residence). In principle, those who have certificates of residence in Japan meet the domestic residency requirement.
- Note: Even those who have certificates of residence in Japan will not satisfy the domestic residency requirement if they clearly do not reside in Japan?for example, those employed overseas.
Exceptions to the domestic residency requirement
Those whose livelihoods are recognized to be based in Japan, such as students studying abroad temporarily, are considered to meet the domestic residency requirement on an exceptional basis, even if they actually reside overseas.
[Cases qualifying as exceptions to the domestic residency requirement]
- (1) Students studying abroad
- (2) Family members accompanying an insured person posted abroad
- (3) Those traveling abroad temporarily for sightseeing, recreation, volunteer activities, or other reasons unrelated to employment
- (4) Those who enter into a family relationship to an insured person while the insured person is posted abroad
- (5) In addition to those described under (1)-(4) above, others whose livelihoods are recognized to be based in Japan in consideration of purposes of traveling abroad and other circumstances
Cases in which a person cannot be certified as a dependent even if he or she resides in Japan
Those who come to Japan on medical visas or on long-stay visas for sightseeing or recreational purposes cannot be certified as dependents, even if they reside in Japan.
Interim measure
As an interim measure, if a person who would lose his or her eligibility as a dependent due to the addition of the domestic residency requirement is hospitalized in a medical care institution in Japan as of the date of enactment of the requirement (April 1, 2020), his or her eligibility will continue during the period of hospitalization.
Dependent certification in cases of joint spousal support (when both spouses work)
In cases of joint spousal support (when both spouses work), the following criteria apply for determining which spouse's dependents the family members will be:
- Regardless of the number of dependent family members, they will be certified as dependents of the insured person with the higher annual income (hereinafter, "annual income" refers to projected income over the coming one-year period, based on past, current, and future earnings).
- If the difference in annual income between both spouses is no more than 10%, then the family members will be certified as dependents of the one of which the Society has been notified as the primary provider.
- If one of the spouses is an insured person under National Health Insurance, then the family members will be certified as dependents of the one with the higher income when comparing the annual income of the insured person under the Health Insurance Society and the projected annual income based on the most recent annual earnings of the insured person under National Health Insurance.
- If one spouse's health insurer does not certify the family members as dependents, a notice of such decision will be issued by the health insurer. The insured spouse of the other health insurer must then attach this notice when applying for dependent certification to the other health insurer.
- When removing the family members as dependents due to a reversal in annual income between the spouses, the deletion must be done only after first confirming that the health insurer of the insured spouse with the higher annual income will certify the family members as dependents.
- If the primary provider takes childcare leave or other leave, the dependent family members will remain dependents during the leave period, as a special measure to ensure the stability of dependent status. (Procedures for dependent certification must be conducted anew for a newborn child.)
If there has been a change in dependents
You must take specific steps if the number of dependents increases due to marriage or childbirth or a family member is no longer eligible as a dependent for reasons such as employment, living apart from the insured person, or death. The Health Insurance Society checks the eligibility status of dependents annually.